DAP-To-Go training packages
Learn how to revolutionize medical technology with the DAP anatomy models!
Discover all courses!

For medical professionals and medical device companies seeking large-format and ultra-realistic anatomical models the Stratasys® J850 Digital Anatomy™ delivers unparalleled capabilities.
Learn how to revolutionize medical technology with the DAP anatomy models!
Discover all courses!
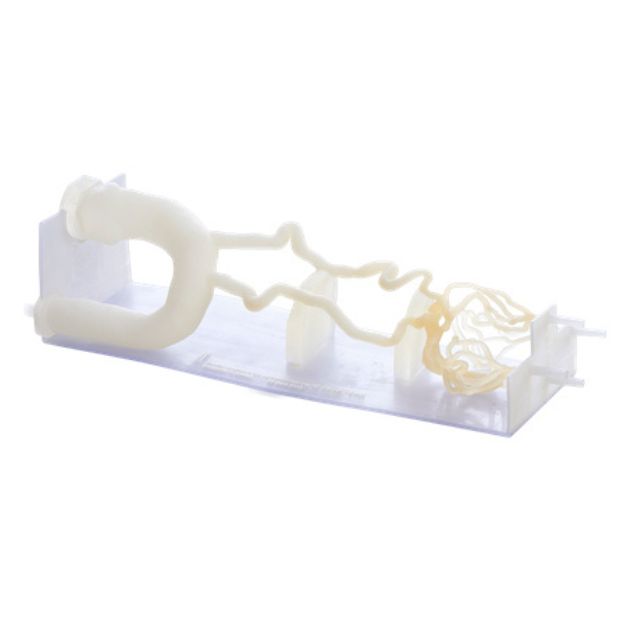
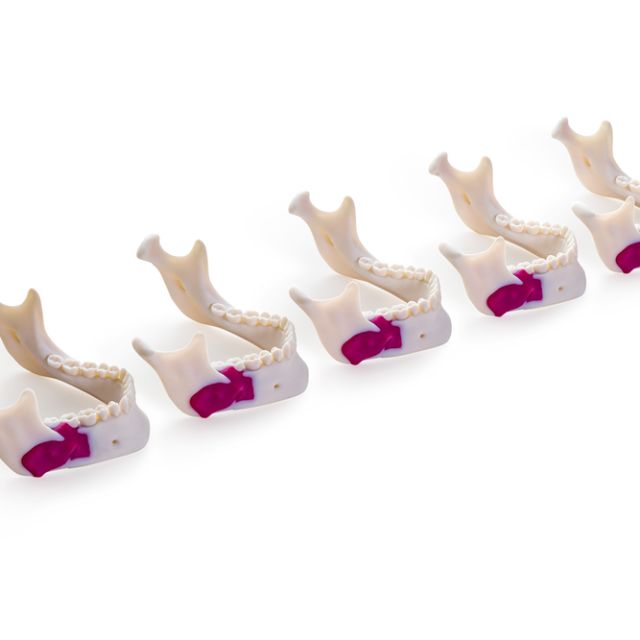
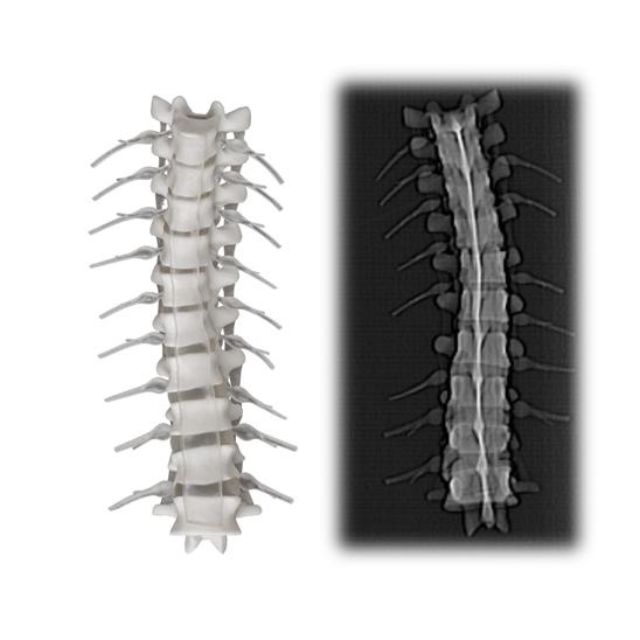
Medical practitioners can work with life-sized replicas that capture complex anatomical details because of the printer's remarkably large build volume of 490 x 390 x 200 mm, which makes it possible to create full-scale anatomical models.
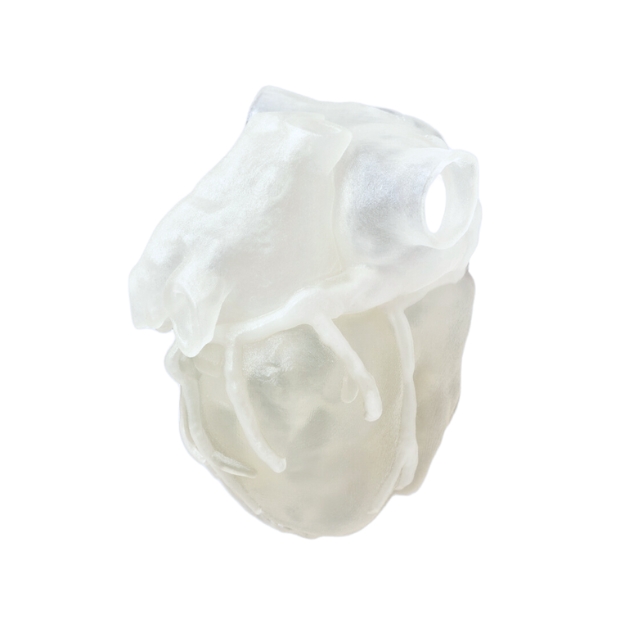
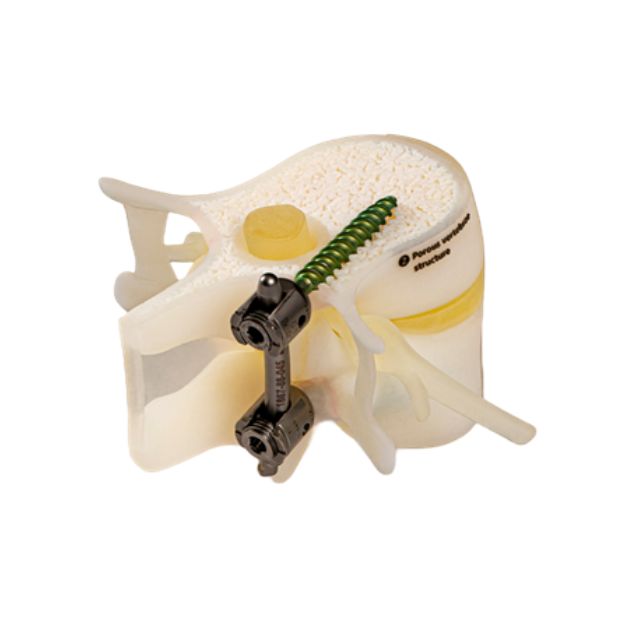
With the use of specific materials (BoneMatrix, GelMatrix, TissueMatrix, and RadioMatrix™) designed to mimic human biological structures, the J850 Digital Anatomy™ 3D printer provides previously unheard-of realism for intricate medical operations like suturing, incision methods, and orthopedic interventions, the printer creates models that offer remarkably accurate haptic input.
In addition, the J850 Digital Anatomy™ enables the creation of radiologically accurate models and phantoms that can be clearly seen with common medical imaging methods such as CT scans and X-rays. The development of large-scale, biomechanically correct models is a major advancement in medical simulation technology that helps close the knowledge gap between theory and practice.
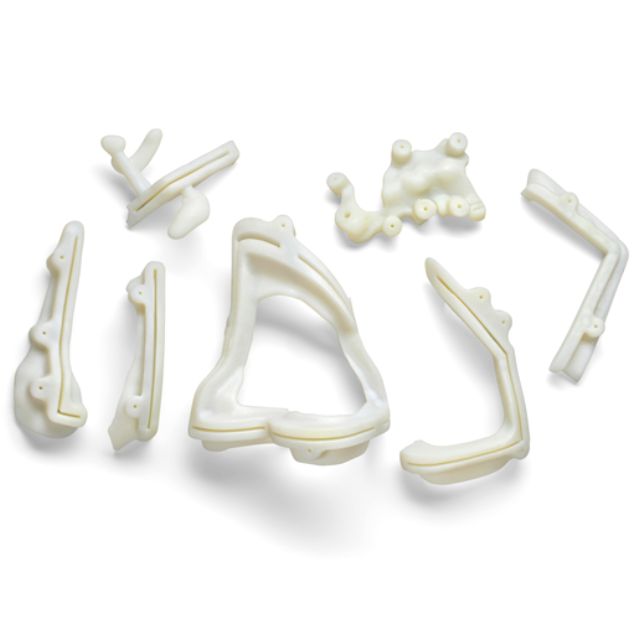
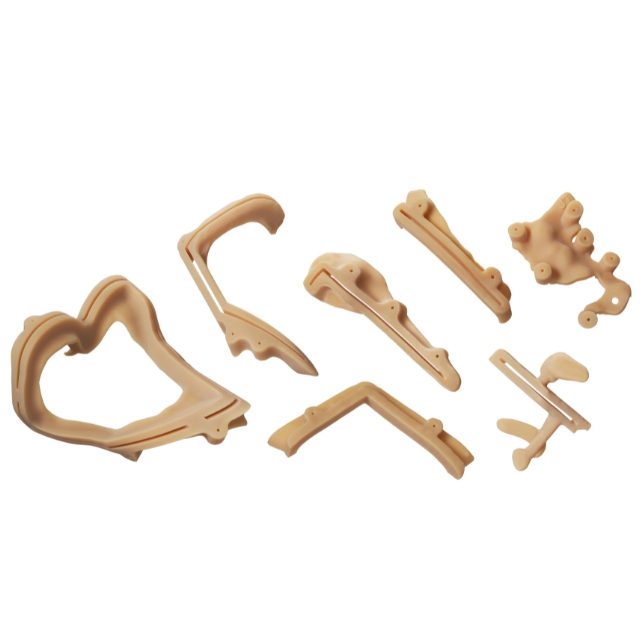
Medical model manufacturing is revolutionized by the J850 Digital Anatomy™'s menu with 100 options and a vast library of more than 1,000 preset anatomical possibilities, which allow for quick, accurate model generation with little operator interaction. To imitate healthy or sick tissue conditions, medical experts can easily choose particular anatomies and modify features, significantly cutting down on the amount of time needed to prepare models.
Unprecedented versatility in producing intricate, multi-material models without frequent material changes is made possible by the printer's novel material storage mechanism, which can hold up to seven distinct materials at once. When building patient-specific models that faithfully capture distinct anatomical variances or disease states, this capability is especially helpful.
Researchers, surgeons, and medical educators can easily create highly customized anatomical models for a variety of purposes thanks to the combination of a large preset selection, multi-material capabilities, and simple customization.
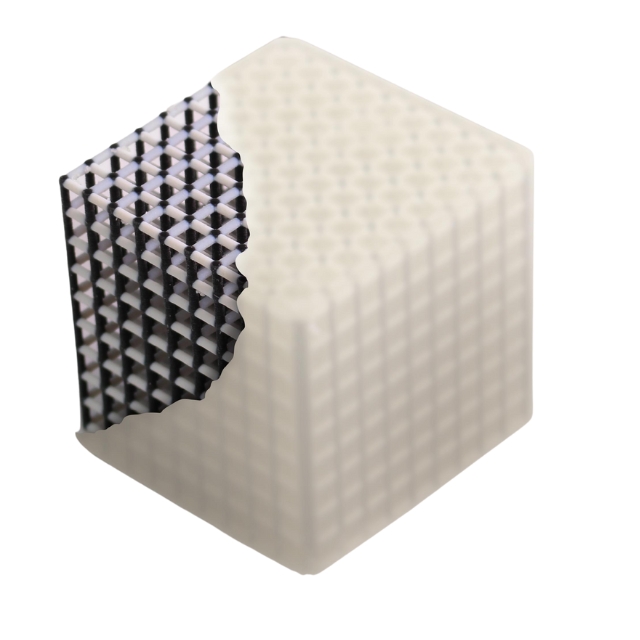
With access to more than 500,000 colors and the capacity to specify complex transparencies, textures, and material finishes, the J850 Digital Anatomy™'s multi-material and full-color capabilities mark a revolutionary advancement in anatomical imaging.
The development of incredibly precise anatomical models that accurately depict the subtle intricacy of human anatomy is made possible by this technological advancement. With the use of color gradients, texture differences, and material transparencies, researchers and educators can now produce models that effectively distinguish between different tissue types, vascular architecture, and disease states.
With its immersive, visually stimulating approach to comprehending human anatomy, this degree of detail revolutionizes medical education and training.
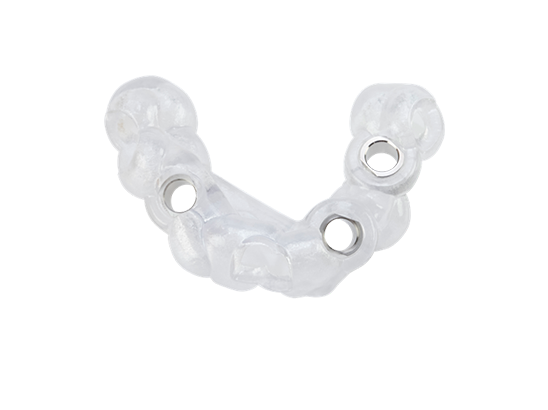
As part of an FDA-approved solution for producing precise anatomical models for diagnostic usage, especially in orthopedic, maxillofacial, and cardiovascular applications, the J850 Digital Anatomy™ printer has obtained 510k clearance and been validated by Synopsys.
It uses biocompatible materials like MED610 and MED615RGD, which may be sterilized by steam, gamma, and EtO methods and are certified for a range of medical applications. Regulatory compliance for medical device manufacture is ensured by the printer's interoperability with FDA-approved software such as Materialise Mimics InPrint and Synopsys Simpleware ScanIP Medical.
The J850 Digital Anatomy™ printer is positioned as a dependable instrument for creating superior, patient-specific anatomical models that satisfy exacting medical industry standards thanks to this thorough certification and validation process.
A cutting-edge approach to cost management and ethical practices in medical education and research facilities is provided by the J850 Digital Anatomy™ printer. Hospitals and university medical facilities can save up to 70% on training costs by keeping a digitized inventory of anatomical models instead of using cadaver and animal labs.
The printer's in-house production of large-scale, multi-material models decreases the logistical difficulties associated with traditional anatomical training resources and does away with the necessity for costly outsourcing.
Beyond economic factors, the technology greatly raises ethical standards by reducing the need for corpse specimens and animal models. This strategy offers a more consistent and repeatable approach to medical education and research in addition to a more economical and sustainable answer.
Produce biomechanically accurate, patient-specific anatomical models for accurate pre-operative planning, which could shorten operating room time while improving patient outcomes.
Create highly lifelike, multi-material anatomical models that aid students and medical professionals understand about complex diseases and structures while providing real haptic feedback.
Make it accessible to rapidly develop and test new medical devices using biomechanically accurate models, which may reduce time to market and remove the need for animal testing.
Make use of the printer's capacity to produce models with tunable radiopacity to produce radio-realistic phantoms for imaging equipment calibration, protocol development, and radiologist training.