3D printers
High quality 3D printers

Simply fill out the form behind the button and receive a free sample of a technology of your choice!
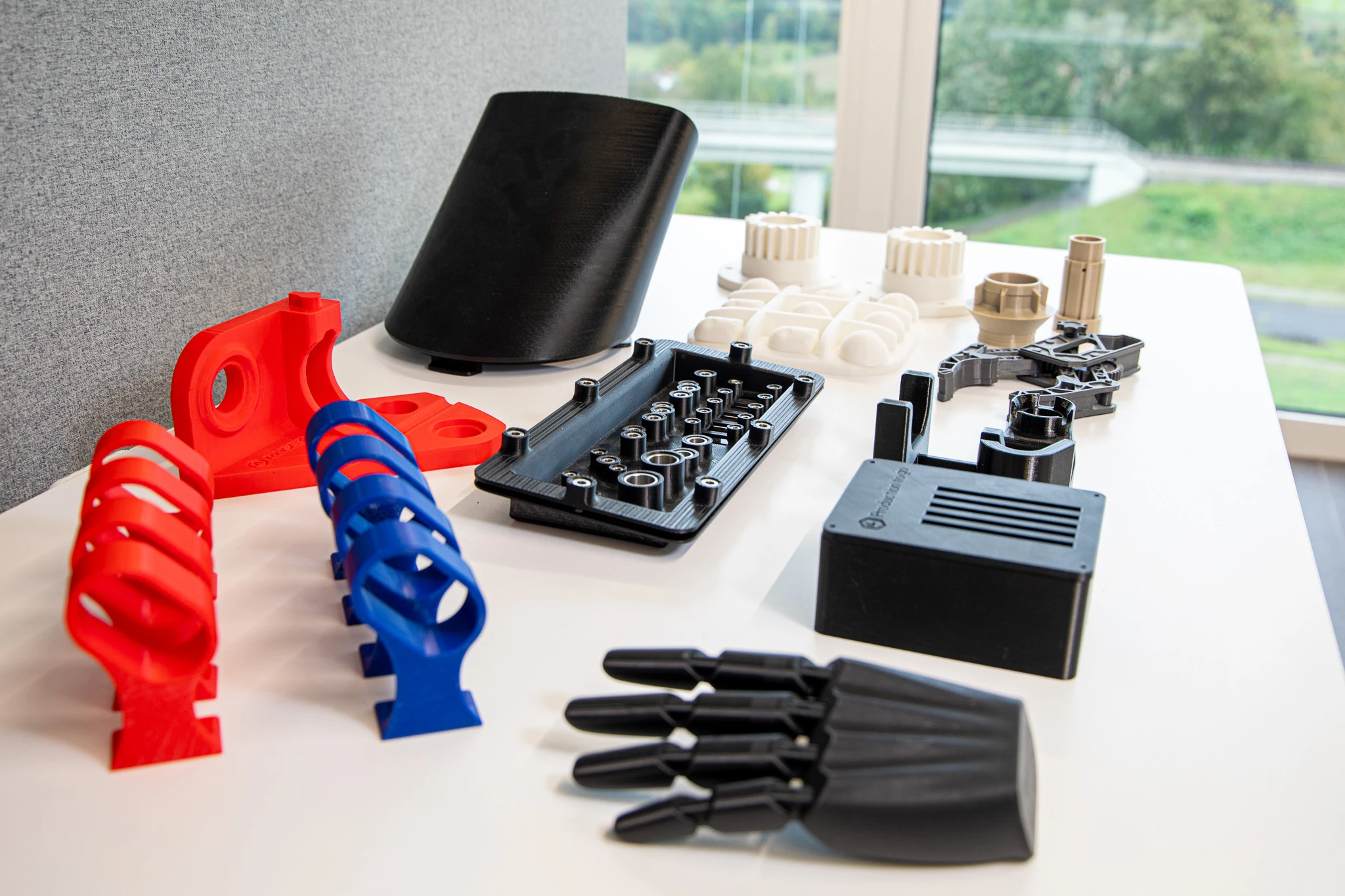

Even if 3D printing with filaments is not the oldest type of 3D printing, it is clearly the best known. In this form of 3D printing, the solid material is fed into the printer and heated above its melting point in the extruder. The now liquid material is then pressed through the extruder and extruded onto the build plate in the desired shape. The hot melt of the extruder melts the surface of the already printed component and the adhesive bond is created. During cooling, the layer bond solidifies and the component is formed.
There are two different processes for this type of 3D printing. The classic process is called fused deposition modelling or fused filament fabrication (FDM or FFF), whereby the two terms are to be used synonymously. The material, the classic filament, is in thread form on a spool, which is inserted into the printer to start the printing process.
The newer technology is called Fused Granular Fabrication (FGF). In contrast to the FDM / FFF process, plastic pellets are used as the starting material rather than filament. This is fed into the printer through a funnel, heated in the extruder and then transported to the nozzle via a screw and finally extruded from the nozzle onto the build plate.
The popularity of this process is partly due to its many advantages. These include the very large selection of materials with many well-known materials, excellent production speeds, very high user-friendliness, low acquisition and material costs and a simple post-processing process.
In the FDM or FFF process, the thermoplastic material is inserted into the printer in filament form and then heated in the extruder and finally extruded through it onto the build plate.
FDM / FFF is very easy and non-toxic to use, has high printing speeds and low costs, but has a rather rough surface and lower resolution.
FGF uses plastic pellets instead of classic filament, which are fed into the printer via a funnel. These are also melted in the extruder and finally extruded onto the build plate.
The FGF process has become particularly popular for large components thanks to the even more favourable material prices and longer uninterrupted printing cycles. However, users sacrifice some detail fineness and material variety in return.
The appropriate CAD or 3D modelling software is used to prepare the digital model and print data. The software also generates the necessary support structures. Finally, the data is transferred to the printer and processed.
Before starting the print job, it must be checked whether there is enough filament for the job. With many systems, it is not possible to change the spool during printing, but with industrial machines it is often possible to use several spools at the same time.
Now the actual printing of the respective component can begin. Layer by layer, the extruder moves along the cross-section of the component and extrudes the liquefied material onto the build plate, where it hardens in the specified shape.
Once the print job is complete, the component is removed from the build plate. The support structures are then removed either by hand, with tools or in a water bath, depending on the support material.
The components can be further processed afterwards, if necessary or as required. For example, they can be painted, coloured or mechanically processed.
In 3D printing with filaments, there are a variety of materials that have received ESD safety certifications and are therefore perfectly suited to the electronics industry and its strict safety regulations. Possible components include electronic housings, antennas, insulators and functional prototypes.

With filament 3D printing, professors and teachers can make their lessons more exciting, more realistic and, in the long term, more cost-effective, as teaching materials can be easily produced on-demand. Possible components include visualisations, anatomy models, prototypes and architectural models.

With a large selection of high-performance materials, the high production speed combined with low costs is perfect for applications in the automotive industry. Possible components include functional prototypes, high-performance moulds, interior fittings and legacy components.

For the consumer goods industry, 3D printing with filaments is suitable for both prototyping and end-use parts, with the wide variety of materials benefiting this technology in particular. Possible components include merchandise, personalised jewellery, footwear and sporting goods.
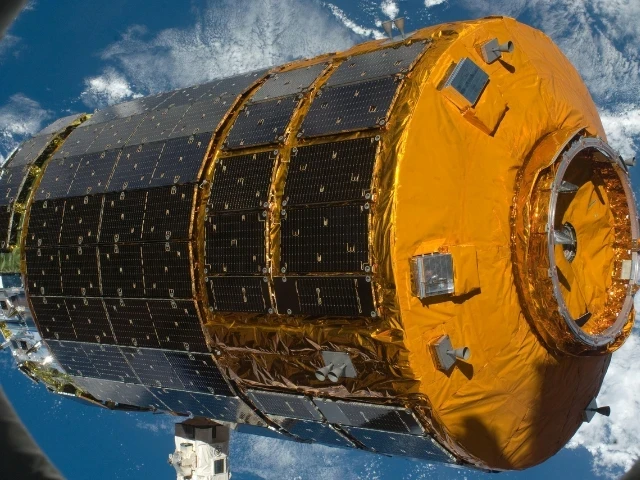

Thanks to the use of aerospace-certified filaments such as PEEK, the very strict safety precautions and regulations of this industry can also be fully met. Possible components include structural parts, high-performance moulds, interior components and prototypes.

Research and development is one of the longest and most intensive phases in the product life cycle. Thanks to filament 3D printing, however, this phase can be massively accelerated and simplified. Possible components include design prototypes, functional prototypes, material development parts and rapid iterations.
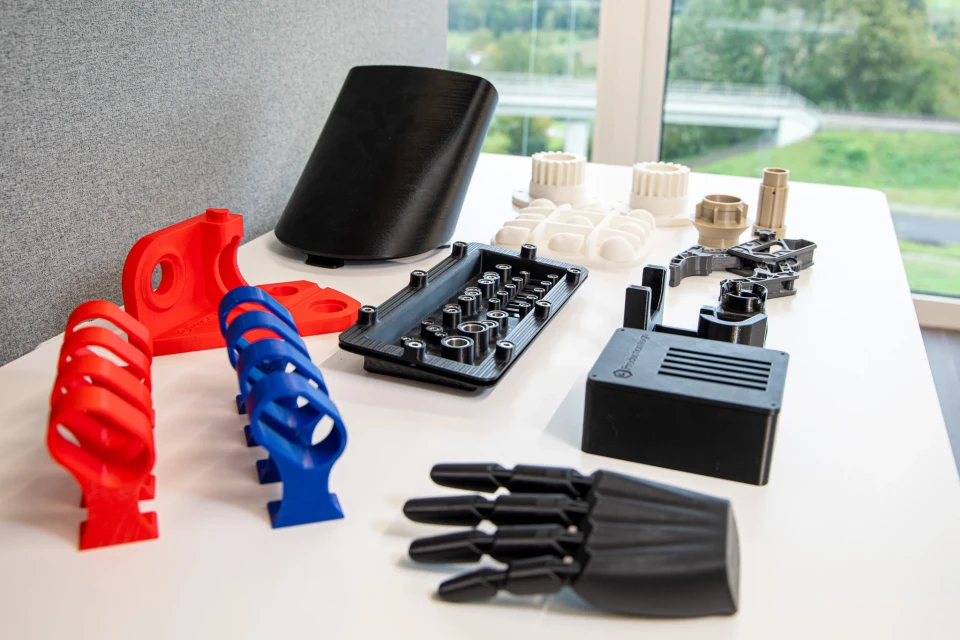


Our team of experts will be happy to support you in choosing the right 3D printing technology and in selecting the right 3D printing system.
Our application team also advises you on the choice of materials. Among other things, we can provide cost and time calculations as well as sample parts. In our showroom we have the possibility to validate the project together with you!
